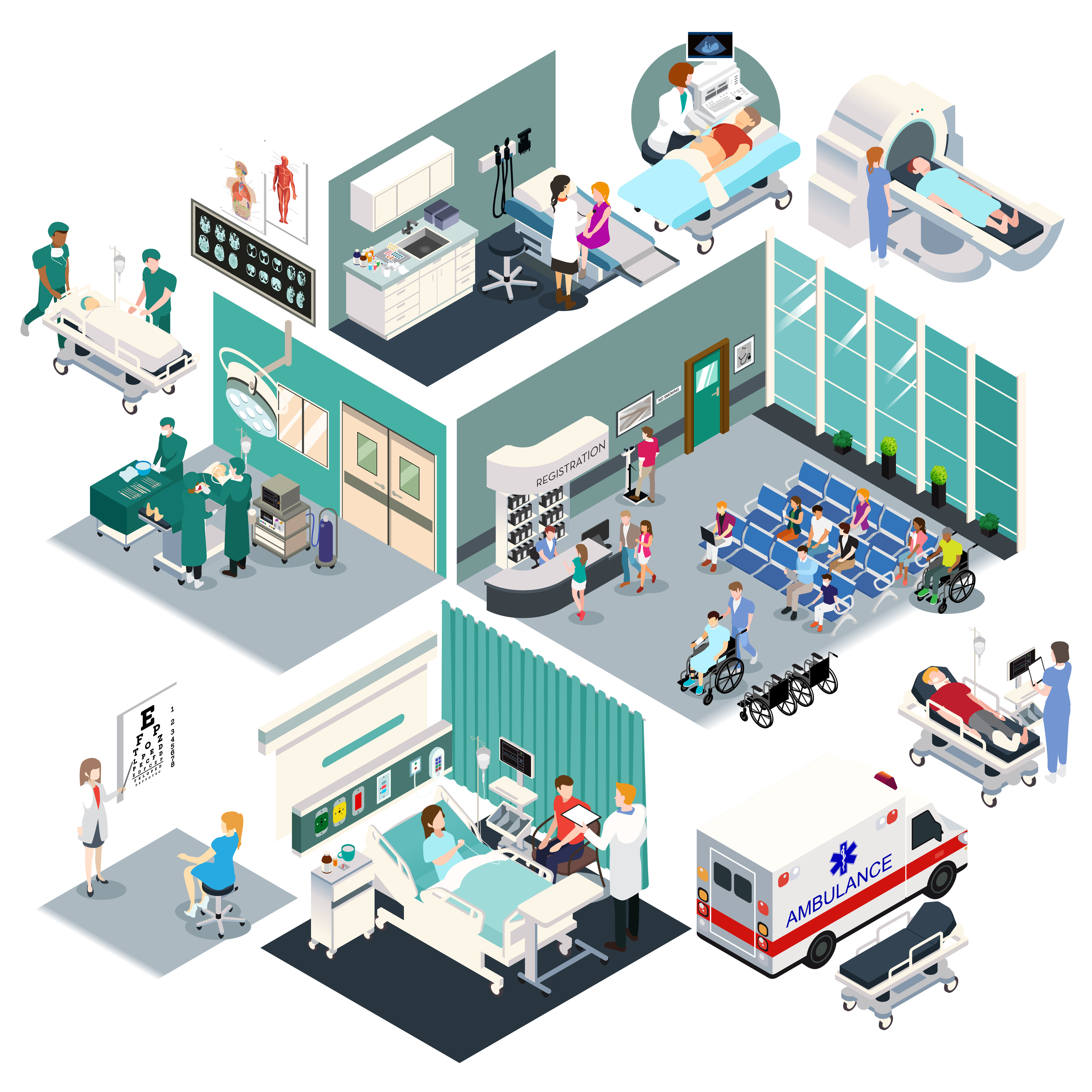
What is the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)?
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is the concept of adding medical devices and software applications into healthcare IT systems, enabling a continuous exchange of medical data and communication and creating a more aware, smart, traceable healthcare experience for patients. This particular segment within the wider scope of the Internet of Things (IoT) concentrates solely on medical device technology tailored for healthcare services.
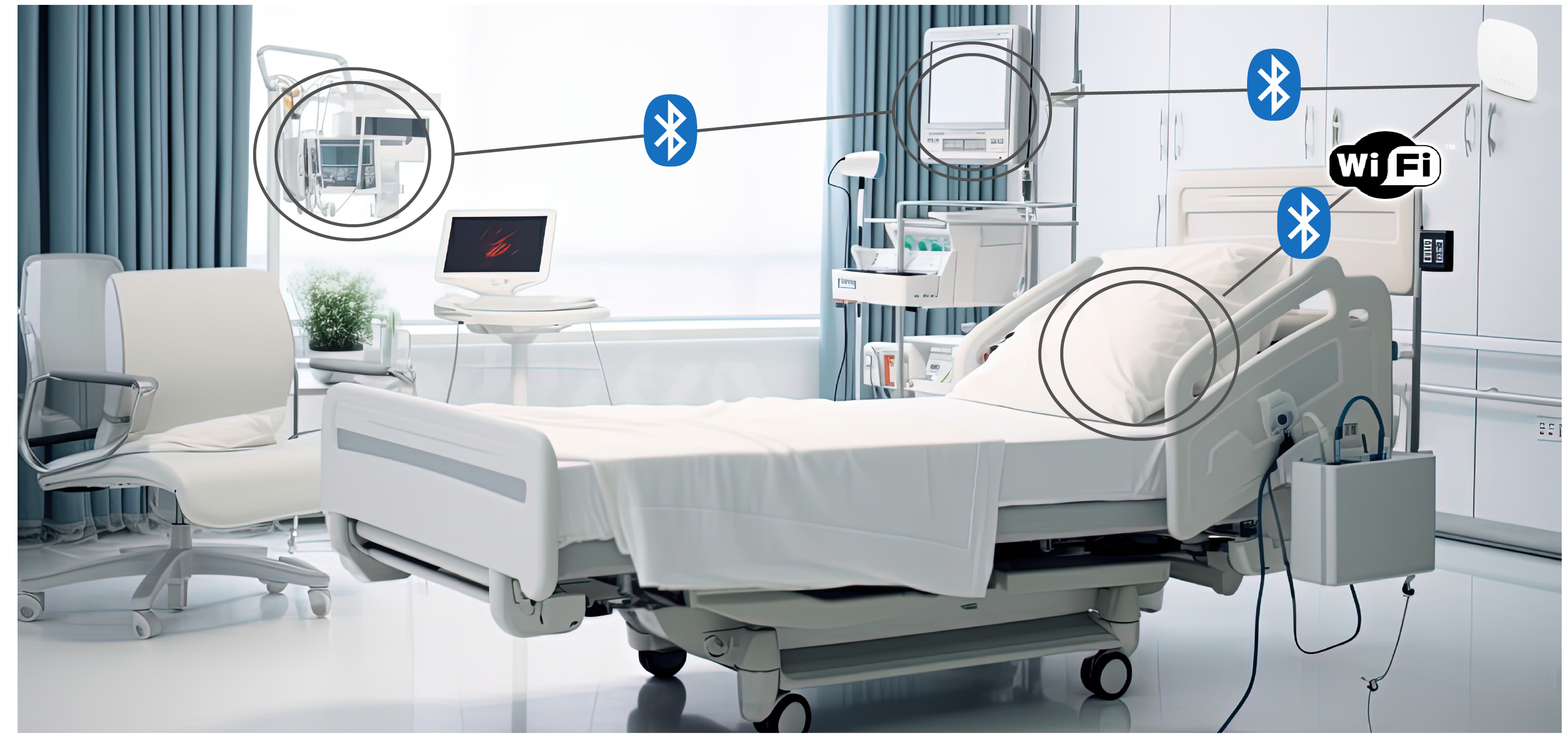
Within diverse environments such as homes, wearables on individuals, community settings, and hospitals, IoMT is catalyzing transformative shifts. Imagine wearable devices that continuously track a patient’s heart rate or intelligent pills relaying information about how well patients follow their medication regimens. These connected Internet devices are not simply speculative ideas, but present realities improving patient care today. By integrating IoMt technologies into these settings, doctors have the ability to do more continuous health monitoring and instantaneously access health data, which assists in easier management of treatment plans.
The swift embrace by the sector toward IoMT technologies has been propelled by both digitalization within healthcare spaces as well as lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak, emphasizing the necessity of remote patient monitoring alongside telehealth provisions—services adeptly supported through IoMT innovations. As key stakeholders like hospitals, device developers and network administrators acknowledge its pivotal function, this trend reflects only growth prospects across professional caregiving scenarios.
Access to more varied and higher volume patient data has already yielded improvements in healthcare. Far better insights become possible, leading directly to better diagnoses and more effective treatments. IoMT allows physicians access to more up-to-date vitals and patient data, equipping physicians with actionable intelligence, better decision-making, and more reliable standards of care.

 Laird Connectivity is now Ezurio
Laird Connectivity is now Ezurio