/filters:background_color(white)/2020-03/Location.jpg)
All About Ultra-Wideband #1: How Is It So Accurate?
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) is a very unique wireless technology. In this series of posts we’re examining what differentiates it from the rest, starting with how it measures location so accurately.
Our line up of innovative new Ultra-wideband modules seamlessly integrate cutting edge UWB silicon from NXP, with the processing and Bluetooth LE capabilities of Nordic Semiconductor’s nRF52 SoC. The combination of the two enables significant advancements in granularity of location that improves existing Bluetooth LE beaconing and RSSI-based ranging. They’re optimised for battery-powered implementations and integrate additional memory, crystals and components to simplify your overall BOM and drive down the cost of integration.
This comprehensive hardware approach is complimented by a range of added value software, Python scripting capabilities, and cloud and mobile tools. Whether your application is hosted or hostless, we have options to suit your application’s needs, as well as your engineering team’s capabilities. All of this is then backed by our industry leading technical support, design services, and test services to to help you simply implement UWB in your next project.
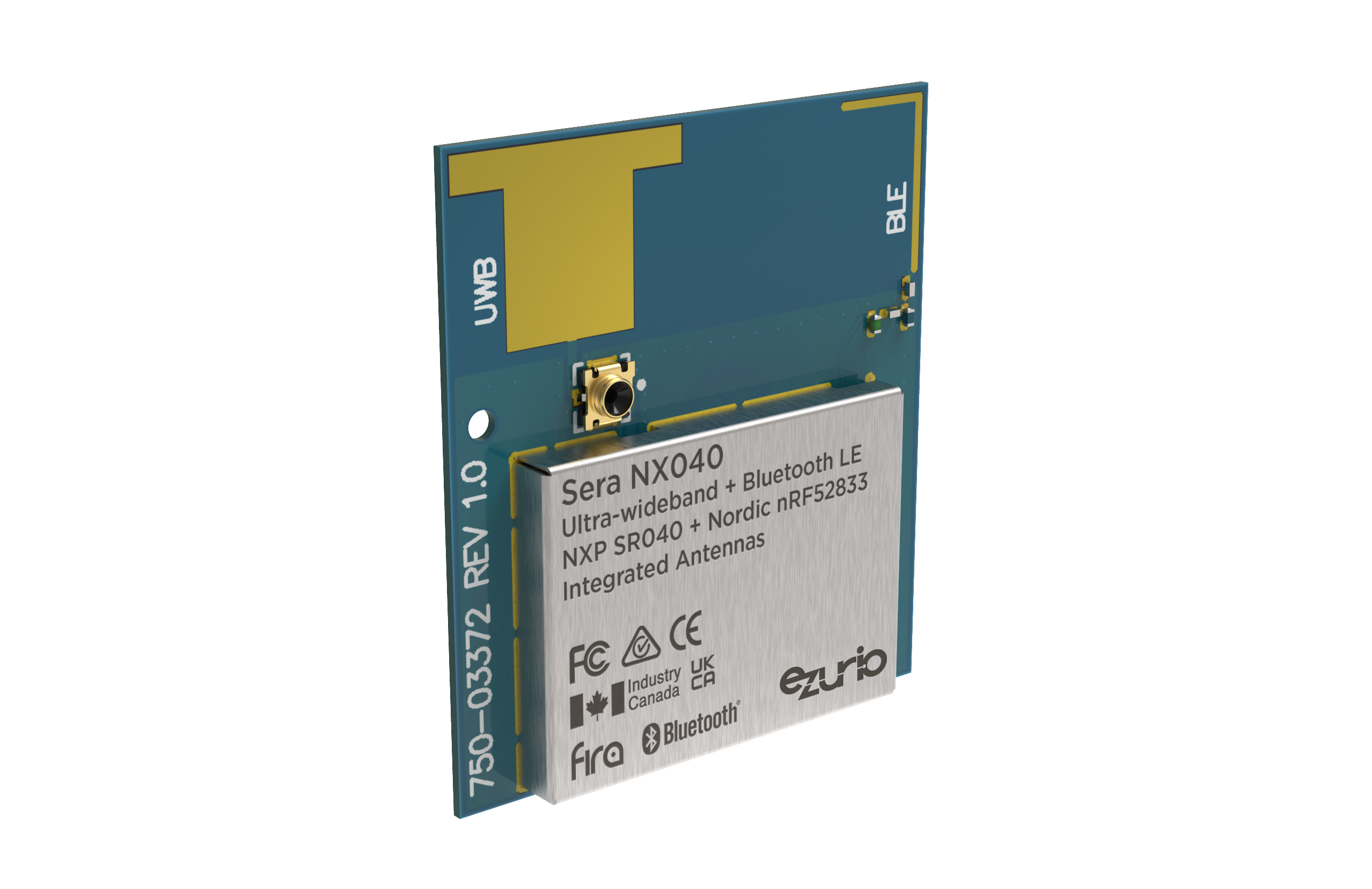

The time has come for Ultra-wideband (UWB) to grow beyond the consumer and automotive segments into mainstream IoT devices. Our innovative integration of the best wireless silicon from NXP and Nordic Semiconductor has produced the secure, flexible Sera NX040 range.
The series features tightly integrated hardware and RF designs, all optimized for low power operation and reducing the need for external clocks, filters and components. Already using Bluetooth LE for basic beaconing or RSSI-based ranging? Now, easily advance to the next level with NFC and UWB for more granular locationing and positioning. This granularity yields much higher accuracy compared to RSSI-only proximity applications in industrial environments.

Ezurio is honored to be approved as an NXP Gold Partner! We look forward to working with the NXP team to deliver the solutions our customers need in an ever changing wireless future. Please follow the link for more information.

Use UWB tags to track machines and equipment on vast factory floors to maximize efficiency and reduce costs. UWB can help factories track the location and movement of valuable assets, such as tools, machinery, and inventory in real time. This enables efficient asset utilization, reduces downtime, and enhances inventory management.
Users can access maps on their smartphones or navigation devices powered by UWB. These highly accurate indoor navigation services can guide people through hospitals, parking garages, and airports. These systems provides real-time guidance, including turn-by-turn directions, to their desired destinations.
UWB can enable quick, accurate tracking of inventory to increase productivity, deter theft, and provide more control of the overall supply chain process. UWB-based tracking can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and the movement of goods throughout the production process.
UWB-based sensors and systems can collect data on various manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization. This data can be used for predictive maintenance, energy efficiency improvements, and process automation.
UWB sensors can be integrated with machinery and equipment to monitor their health and performance. This helps in predicting maintenance needs, reducing unplanned downtime, and extending the lifespan of critical assets.
UWB can be effective for real-time location systems (RTLS) in hospitals to track the movement and location of assets, patients, and personnel. The high precision, low interference, and real time capabilities make UWB an ideal technology for optimizing operations and provide better patient outcomes.
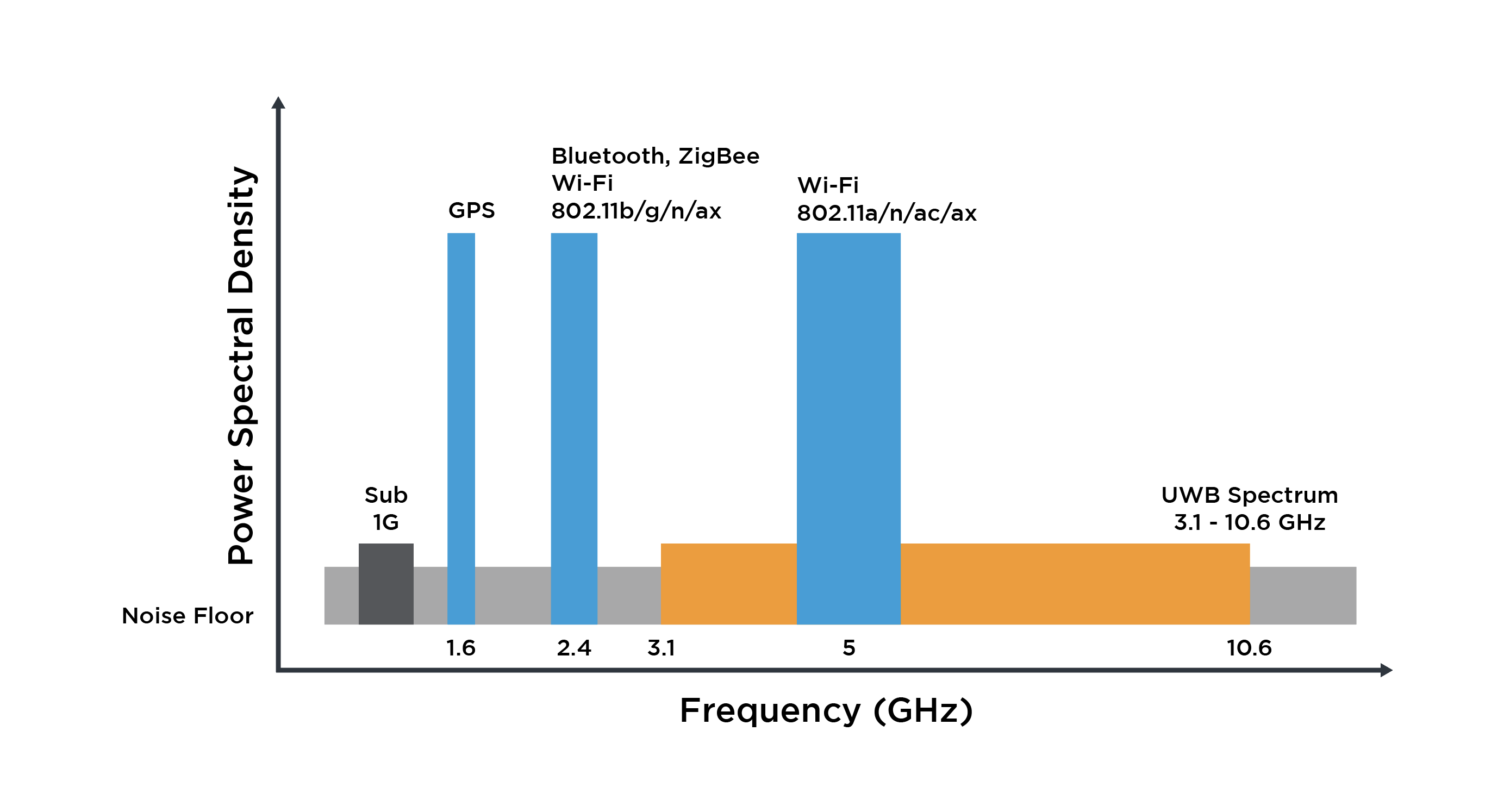
| Technology | Measurement Technique | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth, WiFi | Signal Strength | 7-10m |
| Bluetooth, WiFi | Triangulation | 2-5m |
| WiFi | Time of Flight | 2-5m |
| UWB | Time of Flight | 10cm |
The Nano UWB Series antenna is the first antenna which has been designed to operate with the Sera NX040 UWB module. Ultra-wideband (UWB) is a short-range, high bandwidth wireless technology which enables applications that require high-speed data transfer or for precise location tracking application. UWB transmits and receives signals across an exceptionally broad frequency range.
The Ezurio NanoUWB antenna features a rigid printed circuit board (PCB) that supports UWB implementations. The adhesive backed antenna can be used in space sensitive applications with aesthetically pleasing integration and high durability.

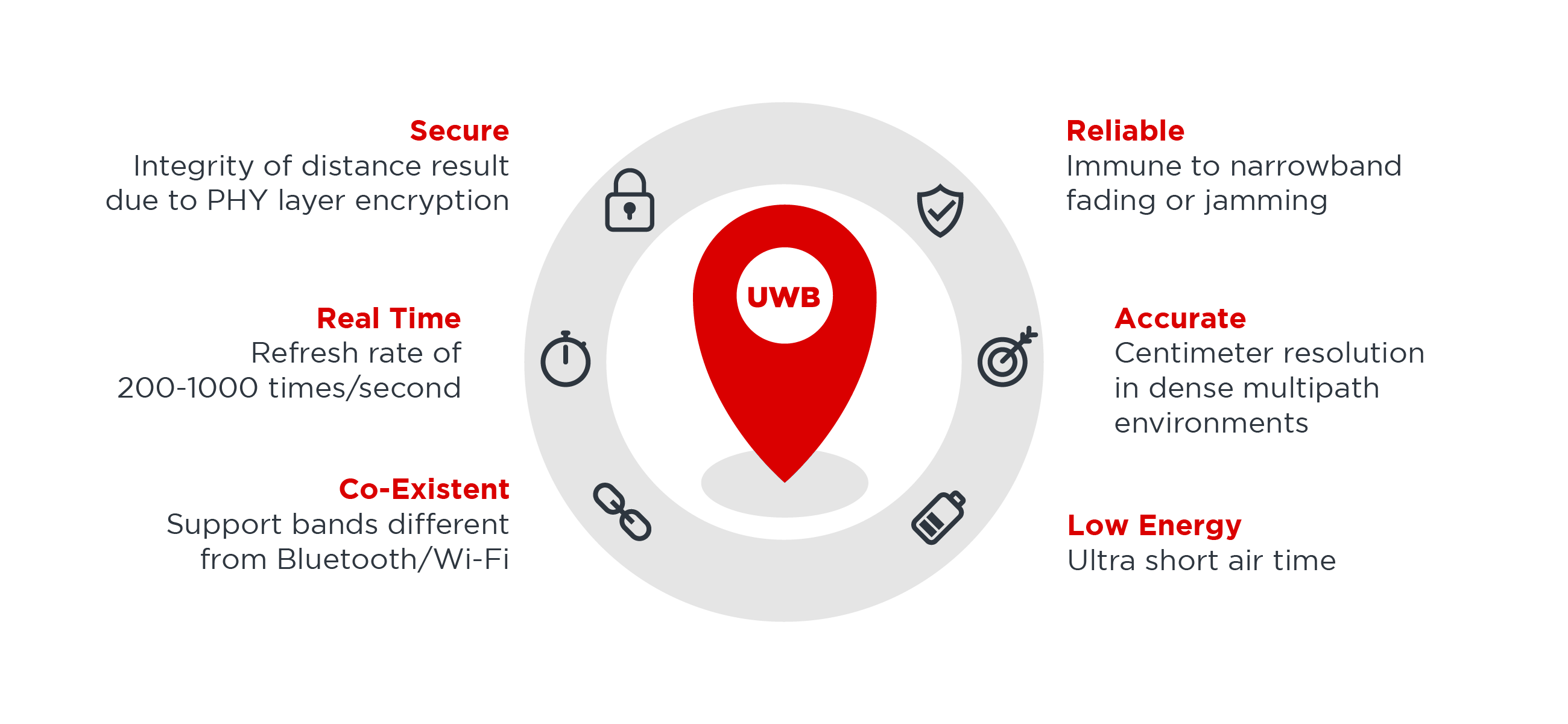
UWB, an abbreviation for Ultra Wide Band, functions as a concise wireless communication protocol for tracking object locations over short distances. Its operation involves pinpointing positions with ~5cm accuracy by gauging the time it takes for brief radio pulses to traverse between two devices.
The functionality of a UWB transmitter revolves around emitting billions of pulses (formerly recognized as "pulse radio") across an expansive frequency spectrum. Subsequently, a corresponding receiver deciphers these pulses into usable data by identifying a recognizable pulse sequence transmitted by the emitter. These pulses are dispatched at a rate of approximately one every two nanoseconds, contributing to UWB's capacity for real-time precision.
UWB exhibits remarkable energy efficiency, while its substantial bandwidth of 500MHz renders it well-suited for transmitting substantial amounts of data from a central device to peripheral ones, covering distances of up to around 30 feet. Nevertheless, unlike Wi-Fi, UWB does not excel in propagating through obstacles such as walls.
UWB Anchors have stationary, predetermined positions registered within the positioning system. They receive signals emitted by UWB Tags. Multiple UWB Anchors capture signals from a single UWB Tag. The system records the time it takes for the signal to travel from the Tag to the Anchor (referred to as Time-of-Flight).
GPS functions as a satellite-oriented navigation system, enabling the determination of a lost item's location over extended distances. On the other hand, UWB, a more recent wireless communication technology, utilizes an expansive bandwidth to furnish precise location details for items that have been misplaced in close proximity.
UWB offers a data-transfer capability with an effective range of up to 25 meters, outperforming its competitor Bluetooth technology, which provides an effective range of only approximately 10 meters.
UWB's precision is restricted to short distances, imposing a limitation on its capacity to be applied across a wider range of scenarios.
Ultra-wideband, often referred to as UWB, ultrawide band, or ultraband, constitutes a short-range wireless communication protocol that harnesses radio waves to facilitate seamless device-to-device communication. While bearing a resemblance to Bluetooth, UWB surpasses it in terms of precision, dependability, and efficiency.
The successful implementation of UWB radar technology hinges on how UWB signals propagate through walls. These signals experience not only attenuation but also distortion due to the dispersive characteristics of the walls when passing through them.
UWB systems exhibit the capacity to monitor a greater quantity of tagged assets across extended distances with heightened precision in comparison to Wi-Fi-based systems. While a Wi-Fi-based Real-Time Location System (RTLS) might ascertain the presence of your assets within a designated room, UWB systems excel in providing precise location details within that room for each individual asset.
/filters:background_color(white)/2020-03/Location.jpg)
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) is a very unique wireless technology. In this series of posts we’re examining what differentiates it from the rest, starting with how it measures location so accurately.
/filters:background_color(white)/2020-03/Location.jpg)
For a technology that inherently involves transmissions with very wide bandwidths, it might be counterintuitive to learn that its transmissions are brief and latency can be so low. We’ll explain why.
/filters:background_color(white)/2020-03/Location.jpg)
In our last post we discussed the ultra-brief pulses that make UWB’s RF behavior unique. In this post, we’ll look at the UWB protocol itself, and the relationship between throughput and power usage.
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/UWB-White-Paper-V2-Cover-1.png)
UWB’s moment in the sun has been a long time coming, which makes its surging use cases and adoption all the more remarkable.
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/Family%20-%20Sera%20NX040%20-%20Embossed%20-%20nxp-nordic.png)
Precise, Granular Positioning and Processing for Medical and Industrial IoT Devices
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/Leveraging%20UWB%20and%20BLE%20in%20Manufacturing%20Environments.png)
Manufacturing processes are being revolutionized by pin-point tracking and monitoring, leading to optimized workflows and enhanced safety protocols within the factory environment.
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-08/uwb-4-click-large_default-11.png)
Our Sera NX040 joins MIKROE’s massive ecosystem of Click boards, which offers countless electronic components with a common connector and extensive software support.
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/Family%20-%20Sera%20NX040%20-%20Embossed%20-%20nxp-nordic.png)
The Sera NX040 delivers precise, granular positioning an processing for medical and industrial IoT devices.
/filters:background_color(white)/2023-09/AdobeStock_1820006341.jpeg)
You’re probably familiar with UWB as the location technology made famous by consumer devices such as Apple AirTags. But this technology is broadly applicable as a solution to MANY problems – and in many industries as well.
/filters:background_color(white)/2024-03/Family%20-%20Sera%20NX040%20-%20Embossed%20-%20nxp-nordic.png)
Python scripts can only be loaded onto a Canvas enabled
device via serial interface such as UART or USB. Canvas FW is programmed over
SWD programming interface only.
Ensure your custom hardware design has provisions for both SWD for Canvas FW programming and serial for loading python scripts.
Review the README.md of the canvas_python_firmware repository (https://github.com/Ezurio/canvas_python_firmware) for the hardware platform to locate the "Default REPL port"
UART1 is used by the Python REPL and is set via Canvas FW running on the module.
No. The nRF Connect SDK is not supported as the SW interface to the NXP SR040 UWB device is not publicly available. The NX040 supports command/response AT Interface or Ezurio Canvas FW with MicroPython scripting for application development.
The module works down to 1.8V and there are no technical issues with using a 1.8V power supply. However, designs may want to consider setting the lower voltage limit as 2.0V as it is possible that a UWB current spike could occur when the host or BLE radio is doing some other function which could potentially cause a brownout/reset on the UWB chip.
Windows should natively support the Sera 040 DVK using CMIS-DAP v2 interface drivers that will appear in device manager under Universal Serial Bus devices.
If in Windows device manager you see an error with CMIS-DAP v2 interface in other devices then it may be that you are using a USB hub or dock that is preventing Windows from properly identifying the Sera 040 DVK. In which case try plugging the DVK directly into a USB port on your laptop or PC and it should be discovered automatically
At the time of writing there may be issues installing pyocd for Python 3.12. If you experience issues such as failing to build wheel for hidapi, try reverting to Python 3.10 or 3.11.
We have also seen issue where pyocd reports an error during install, requiring VS C++ build tools. Be sure to install the C++ build tools using the link in the error. If the C++ build tools install fail then try to temporarily disable virus checking (or consult with your IT department) as we have seen some antivirus block some VS scripts used during build tool installation.
Data transfer over the UWB channel is not currently supported by NXP's firmware that is loaded to Laird's Sera NX040 UWB tag.
Laird's NX040 has an accuracy of +/-10cm for two-way ranging.
The functionality of a UWB transmitter revolves around emitting billions of pulses (formerly recognized as "pulse radio") across an expansive frequency spectrum. Subsequently, a corresponding receiver deciphers these pulses into usable data by identifying a recognizable pulse sequence transmitted by the emitter. These pulses are dispatched at a rate of approximately one every two nanoseconds, contributing to UWB's capacity for real-time precision.
UWB exhibits remarkable energy efficiency, while its substantial bandwidth of 500MHz renders it well-suited for transmitting substantial amounts of data from a central device to peripheral ones, covering distances of up to around 30 feet. Nevertheless, unlike Wi-Fi, UWB does not excel in propagating through obstacles such as walls.
UWB Anchors have stationary, predetermined positions registered within the positioning system. They receive signals emitted by UWB Tags. Multiple UWB Anchors capture signals from a single UWB Tag. The system records the time it takes for the signal to travel from the Tag to the Anchor (referred to as Time-of-Flight).
GPS functions as a satellite-oriented navigation system, enabling the determination of a lost item's location over extended distances. On the other hand, UWB, a more recent wireless communication technology, utilizes an expansive bandwidth to furnish precise location details for items that have been misplaced in close proximity.
UWB offers a data-transfer capability with an effective range of up to 25 meters, outperforming its competitor Bluetooth technology, which provides an effective range of only approximately 10 meters.
The successful implementation of UWB radar technology hinges on how UWB signals propagate through walls. These signals experience not only attenuation but also distortion due to the dispersive characteristics of the walls when passing through them.
UWB's precision is restricted to short distances, imposing a limitation on its capacity to be applied across a wider range of scenarios.
UWB systems exhibit the capacity to monitor a greater quantity of tagged assets across extended distances with heightened precision in comparison to Wi-Fi-based systems. While a Wi-Fi-based Real-Time Location System (RTLS) might ascertain the presence of your assets within a designated room, UWB systems excel in providing precise location details within that room for each individual asset.
Ultra-wideband, often referred to as UWB, ultrawide band, or ultraband, constitutes a short-range wireless communication protocol that harnesses radio waves to facilitate seamless device-to-device communication. While bearing a resemblance to Bluetooth, UWB surpasses it in terms of precision, dependability, and efficiency.
UWB, an abbreviation for Ultra Wide Band, functions as a concise wireless communication protocol for tracking object locations over short distances. Its operation involves pinpointing positions with ~5cm accuracy by gauging the time it takes for brief radio pulses to traverse between two devices.
fira is the industry consortium that defines the UWB ranging specification and certifies products for the purposes of interoperability. The name stands for "fine ranging".
There are various levels of fira membership as listed at the link below
Ezurio is an adopter member of fira.
fira membership is required to access specifications (fira intellectual property) and to certify end products.